Hyper-V is Microsoft's in-house virtualization solution for Windows 11. It lets you create virtual machines and run them on virtual hardware. That said, if you want to use Hyper-V on your PC, you'll need to enable it first.
In this article, we show you the three ways to enable Hyper-V in Windows 11 and create virtual machines without third-party tools.
What are the use cases for Hyper-V?
Hyper-V is a native virtualization tool that lets you run multiple operating systems on their own virtual machines.
With Hyper-V, you don't have to rely on third-party hypervisor solutions like VirtualBox and VMware WorkStation. It limits your choice of guest operating system to Windows, Linux, and FreeBSD.
Some Hyper-V virtual machine use cases include:
- Run and test software for an older version of Windows or a non-Windows operating system
- Test software on multiple operating systems using multiple virtual machines on a single host system.
Prerequisites to enable Hyper-V on Windows 11
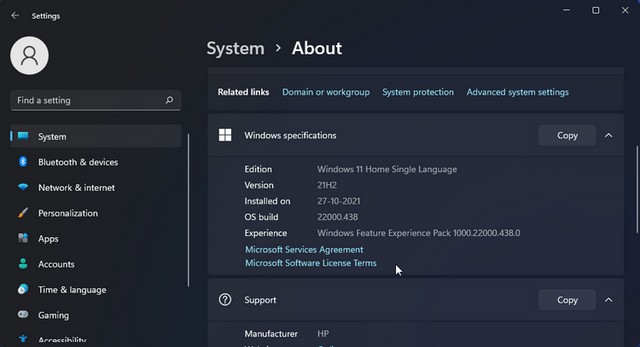
Hyper-V is available as an optional feature on Windows 11 Pro, Enterprise, and Education. To check your edition of Windows, go to Settings > System > About . Then, check the Windows specs section to find your Windows edition.
If you have the Home edition, here's how to install Hyper-V on Windows 11 Home. All you have to do is run a bat script to install Hyper-V on unsupported systems.
Depending on the number of virtual machines and the types of applications you intend to run, you may need more resources to run the virtual machines smoothly.
Additionally, you need to enable hardware virtualization in the BIOS. This is an essential feature for running virtual machines on your Windows system but often disabled by default.
How to Enable Hardware Virtualization in BIOS
On compatible systems, you can enable hardware virtualization in the BIOS. The steps below are for an HP computer. If you are using a custom-built PC or laptop from another manufacturer, refer to the user manual for detailed instructions. Otherwise, refer to our general guide to entering BIOS in Windows .
To enable hardware virtualization in BIOS:
- Shut down your PC if it is on.
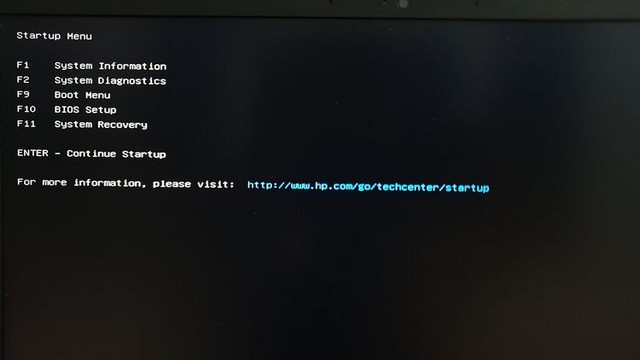
- Press the power button to turn on the system and start pressing the escape key to bring up the boot menu .
- From the Boot Menu , press F10 to enter BIOS Setup .
- In the BIOS Setup Utility, use the arrow key and open the Setup tab .
- Next, use the down arrow key to highlight the Virtualization Technology option .
- Press Enter , then select Enabled from the options.
- Press F10 to save changes and exit BIOS .
- Your PC will restart and apply the changes. This may take a while, so wait until your system is completely restarted.
After restarting, you can enable Hyper-V on Windows 11. Here's how to do it.
1. Enable Hyper-V in Windows 11 via Control Panel
You can enable Hyper-V using the Windows Features dialog. You can access Windows Features to add or remove optional features in Windows 11 from Control Panel. Here's how.
- Press Win + R to open Run .
- Type control and click OK to open the Control Panel.
- In Control Panel, go to Programs > Programs and Features .
- In the left pane, click Turn Windows features on or off .
- Now, in the Windows Features dialog , select Hyper-V . If you are developing Hyper-V, you will see Hyper-V Management Tools and Hyper-V Platforms .
- Make sure both options are selected and click OK . Since these are optional features, Windows will start installing and activating them on your PC. This process may take some time.
- When done, click Restart Now to restart and apply the changes.
After restarting, search for Hyper-V and click Hyper-V Manager to create virtual machines in Windows 11.
2. Add Hyper-V to Windows 11 using Command Prompt
The command prompt offers a fast and efficient way to perform repetitive tasks. You can use the DISM (Deployment Image Servicing and Management) command-line tool to access and install Windows optional features through the command prompt.
Follow these steps to enable Hyper-V on Windows 11 using Command Prompt:
- Press the Win key and type cmd . Next, right-click on Command Prompt and select Run as administrator .
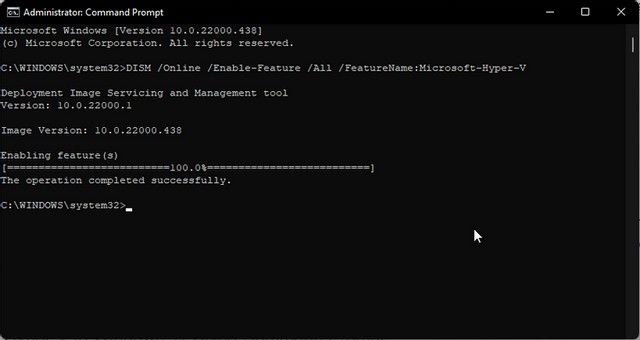
- In the Command Prompt window, type the following command and press Enter to run:
- The Deployment Image Servicing and Management Tool will begin to enable Hyper-V functionality and show the progress on the command prompt.
- Once the operation is completed successfully, you will need to restart your PC. So, press Y on your keyboard to confirm the action.
After your PC restarts, you can open and use Hyper-V Manager to create virtual machines.
3. Enable Hyper-V using PowerShell
If you prefer Windows PowerShell over the command prompt, you can also enable Hyper-V using the shell application.
However, unlike the command prompt, PowerShell uses the enable-WindowsOptional features cmdlet to enable optional features in a Windows image.
To enable Hyper-V with PowerShell:
- Press the Win key and type powershell . Next, right-click on PowerShell and select Run as administrator .
- In the PowerShell window, type the following shell command and press Enter:
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName Microsoft-Hyper-V -All- PowerShell will run the cmdlet and start the Hyper-V activation process. If successful, you will be asked to restart your PC.
- Type Y to confirm and your PC will restart to apply the changes and activate a new feature.
Multiple Ways to Enable Hyper-V in Windows 11
Hyper-V is a Type 1 hypervisor, meaning it runs directly on a computer's hardware. It comes pre-installed, can be used for free without restrictions, and provides linear performance on a mainstream system.
That said, dedicated virtual machines like VMWare WorkStation Pro are available on multiple platforms, can be used on older systems, and are better suited for enterprise solutions. Check out our comparison comparing the three popular hypervisors to find the right one for you.